京东健康互联网医院
京东健康互联网医院
 网站导航
网站导航

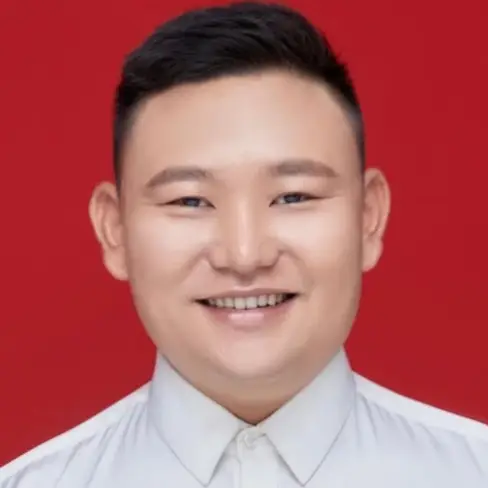
古丈县人民医院位于古阳镇广场社区,始建于1952年,历经半个多世纪的变革与发展,现已发展成为我县唯一集医疗、预防、保健、教学为一体的综合性二级医院,肩负着全县14万多人民以及周边县市邻近地区人民的医疗保健和疾病救治任务,并且是我县120急救中心,县孕产妇抢救中心,县中心贮血点。医院占地总面积1.08万平方米,其中业务用房建筑面积1.9万平方米,其中常德市援建4200平方米。目前定编床位180张,实核人员编制188人。医院现有职工278人,卫生专业技术人员228人,其中副高级职称10人,中级职称65人(其中临床医疗7人)。现开设内科(肾内科、肿瘤科)、外科、儿科(新生儿科)、妇产科、急诊科(内二科)、麻醉手术科、血液透析中心、检验科、放射科、药剂科、功能科等14个临床医技科室及第一、第二两个门诊部。2005年—2008年常德市第一人民医院先后多次共派出6批17名专家来古丈县人民医院帮扶带教,并免费培养专业技术人员10人,于2019年选派一名业务骨干来院挂职任副院长。随着标准化医院建设步伐的加快,医院各项设施逐步完善,目前医院已引进HIS、LIS、PACS、EMR四大系统,实现了信息化管理;拥有16排CT、血液透析机、全自动清洗消毒机、脉动真空灭菌器、多功能彩超、B超、电子胃镜、全自动生化分析仪、全自动五分类血计数仪、多功能麻醉机、美国鸟牌呼吸机、DR、多参数心电监护仪、新生儿恒温箱、耳声发射检测仪、组织切片机、电视腹腔镜、电子阴道镜、母婴监护仪、进口利普刀等万元以上医疗设备30多台件。2018年门诊病人97377人次,入院病人7046人次,出院7107人次,手术台次954台次。在上级各部门的大力支持下,我院发展取得了长足进步,就医条件及服务能力有了明显的改善,目前基本上能满足古丈县及周边县市人民的就医需求。是由人乳头瘤病毒感染所引起的皮肤表面良性赘生物,人乳头瘤病毒感染,身体任何部位,不是所有疣都需要治疗,药物治疗,去除疣体,疣状皮肤结核,鸡眼,点状掌跖角化症,毛囊上皮瘤,汗管瘤,扁平苔藓,正常饮食即可,无需忌口,皮肤镜检查,。
 0
0

紫疣的治疗,除了冷冻还可以选择温热治疗。温热治疗是最近两年刚刚出来的,也是中国医科大学附属第一医院高新化团队的科研成果。它的效果真的非常不错,对以前觉得意想不到的,比较难治疗的紫疣,通过红外产生出来的高温,大概温度是42度-46度之间,它可以调动机体的主动免疫来杀灭病毒,所以这是非常科学的主动治疗的方法,治愈率非常的高。当然,还可以选择激光,选择联合外用药、口服药物来治疗,效果都是可以的。
 10
10

病毒疣,也就是疣的统称。它是由于人体感染上人乳头瘤病毒(HPV)而引起的皮肤增生性损害疾病,通常表现为表面长出赘生物,呈菜花状、鸡冠状、乳头状、条索状、桑葚状等多样的外观,并且具有较强的传染性。病毒疣的种类比较多,部分疣可能出现自行愈合的情况。对于该病的治疗,以外用药、二氧化碳激光、液氮冷冻、电灼或者手术等比较常见。而不同的疣类疾病,治疗难度和危害性也不一样。那么,就让我们以比较严重的病毒疣尖锐湿疣为例,来给大家科普一下如何治疗该病才能去根的问题。

 5
5

流行病学
皮肤型的 HPV 人群感染率非常普遍,如上述常见的寻常疣、趾疣、扁平疣等,无法得到具体的感染率,比较引起注意到是高危型的 HPV 感染和外生殖器的低危型 HPV 感染造成的生殖器疣和宫颈癌,据统计在全球的性病中,HPV 感染引起的生殖器疣占 15-20%。
关于女性生殖道感染 HPV 的流行情况,据 2003-2004 年来自美国的国家健康和营养研究课题的一个调查结果显示,14-59 岁的 HPV 总感染率为 26.8%,所以 HPV 感染在女性造成的负担超出之前的估计。我国的 HPV 感染的流行病学筛查未见大样本的报告,但是由 HPV 感染造成的性病中的尖锐湿疣的发病率在迅速上升,估计发病率应该是性病中最多的,因为存在大量的漏报和不报。我国每年约有 13.15 万新发现的宫颈癌,报告中发病率和死亡率有增加趋势,且宫颈癌发病年龄年轻化,可以预见 Hpv 感染造成在我国造成的损失的巨大.[5] [3] [4] [6]
 33
33
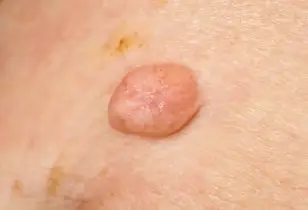
病毒疣的发生可以长在任何部位,也叫寻常疣,它是由乳头瘤病毒引起的。如果发生在手部,指甲的周围,治疗起来相对来说比较困难一点。尤其在甲周围,这种病毒疣是很难处理的。需要搞好个人卫生,增强体质。病毒的感染多数和自身免疫力有关系的,一定要讲好个人卫生。
那么对于病毒疣的治疗,对不同的年龄,方案也可以不一样,耐受力也可能不太一样,所以要选择不同的治疗的方法。
第一,外用药物。可以外用咪喹莫特、疣立消,还有一些消疣灵都是可以外用的。像疣立静制剂,即可达到剥脱抗病毒的作用。口服一些调节免疫力的药物,像转移因子都是可以的。
第二,物理治疗。可以采用冷冻治疗,冷冻治疗就是略有疼痛,它是用低温液氮,低温导致病毒的坏死;也可以采用二氧化碳激光进行治疗。
第三,光动力联合一些手术治疗的方法。
 28
28
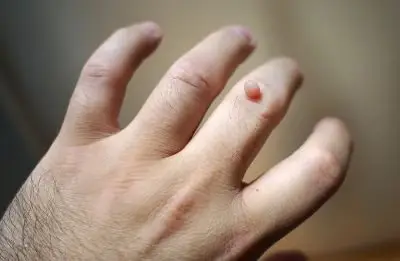

疣为人乳头瘤病毒感染所致,可通过直接或间接接触传染。肛周、生殖器疣大多通过性接触传染,外伤或皮肤破损是HPV感染的重要因素。免疫力低下也是疣产生的重要原因。
疣的分类? 根据临床表现及症状,疣常见的可以分为寻常疣、扁平疣、跖疣、生殖器疣(尖锐湿疣)等。

疣的预防
1、患者应多食新鲜的蔬菜、水果补充维生素,少食鱼、虾、蟹以及辛辣刺激性食物。
2、不要自行盲目使用药物及其他治疗方法,以免造成泛发。
3、不要搔抓或抠剥疣体,洗澡时不宜过度搓洗以免自身接种。
4、由于疾病具有传染性,应注意个人卫生,忌与他人共用清洁用具,避免交叉感染。平时加强锻炼,提高身体素质。
疣的治疗
1、物理疗法:激光、冷冻、电灼、微波、光动力和手术切除等都属于物理方式,一般可以较快地去除局部疣体,去疣效果明显,但难以清除表皮细胞棘层、基底层的HPV病毒。
2、化学疗法:化学药物治疗尖锐湿疣,多数情况下属于腐蚀性药物,通过强腐蚀性消除疣体。该方法使用要谨慎,不小心容易灼伤到正常健康的皮肤组织。
3、免疫疗法:通过提高人体或患处局部的免疫力,从而达到抑制HPV病毒复制,阻碍病情发展的目的。一般多用于辅助治疗,如干扰素、生长因子等。
4、中医治疗:中医理论认为,湿疣是湿热下注、外侵肝经、湿热内蕴所致的皮肤“臊瘊”,根据个人体质和病情合理组方,熬制汤剂,中药泡洗、或者火针等有针对性地进行治疗,去疣清毒,就可以达到根治目的。
 0
0

以下内容来源于新英格兰医学杂志。



 0
0

以下内容来源于新英格兰医学杂志。
Presentation of Case
Dr. Christine M. Parsons (Medicine): A 75-year-old woman was evaluated at this hospital because of arthritis, abdominal pain, edema, malaise, and fever.
Three weeks before the current admission, the patient noticed waxing and waning “throbbing” pain in the right upper abdomen, which she rated at 9 (on a scale of 0 to 10, with 10 indicating the most severe pain) at its maximal intensity. The pain was associated with nausea and fever with a temperature of up to 39.0°C. Pain worsened after food consumption and was relieved with acetaminophen. During the 3 weeks before the current admission, edema developed in both legs; it had started at the ankles and gradually progressed upward to the hips. When the edema began to affect her ambulation, she presented to the emergency department of this hospital.
A review of systems that was obtained from the patient and her family was notable for intermittent fever, abdominal bloating, anorexia, and fatigue that had progressed during the previous 3 weeks. The patient reported new orthopnea and nonproductive cough. Approximately 4 weeks earlier, she had had diarrhea for several days. During the 6 weeks before the current admission, the patient had lost 9 kg unintentionally; she also had had pain in the wrists and hands, 3 days of burning and dryness of the eyes, and diffuse myalgias. She had not had night sweats, dry mouth, jaw claudication, vision changes, urinary symptoms, or oral, nasal, or genital ulcers.
The patient’s medical history was notable for multiple myeloma (for which treatment with thalidomide and melphalan had been initiated 2 years earlier and was stopped approximately 1 year before the current admission); hypothyroidism; chikungunya virus infection (diagnosed 7 years earlier); seropositive erosive rheumatoid arthritis affecting the hands, wrists, elbows, and shoulders (diagnosed 3 years earlier); vitiligo; and osteoarthritis of the right hip, for which she had undergone arthroplasty. Evidence of gastritis was reportedly seen on endoscopy that had been performed 6 months earlier. Medications included daily treatment with levothyroxine and acetaminophen and pipazethate hydrochloride as needed for cough. The patient consumed chamomile and horsetail herbal teas. She had no known allergies to medications, but she had been advised not to take nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs after her diagnosis of multiple myeloma.
Approximately 5 months before the current admission, the patient had emigrated from Central America. She lived with her daughter and grandchildren in an urban area of New England. She had previously worked in health care. She had no history of alcohol, tobacco, or other substance use. There was no family history of cancer or autoimmune, renal, gastrointestinal, pulmonary, or cardiac disease.
On examination, the temporal temperature was 37.1°C, the heart rate 106 beats per minute, the blood pressure 152/67 mm Hg, and the oxygen saturation 100% while the patient was breathing ambient air. She had a frail appearance and bitemporal cachexia. The weight was 41 kg and the body-mass index (the weight in kilograms divided by the square of the height in meters) 15.2. Her dentition was poor; most of the teeth were missing, caries were present in the remaining teeth, and the mucous membranes were dry. She had abdominal tenderness on the right side and mild abdominal distention, without organomegaly or guarding. Bilateral axillary lymphadenopathy was palpable. Infrequent inspiratory wheezing was noted.
The patient had swan-neck deformity, boutonnière deformity, ulnar deviation, and distal hyperextensibility of the thumbs (Fig. 1). Subcutaneous nodules were observed on the proximal interphalangeal joints of the second and third fingers of the right hand and on the proximal interphalangeal joint of the fourth finger of the left hand. Synovial thickening of the metacarpophalangeal joints of the second fingers was noted. There was mild swelling and tenderness of the wrists. She had pain with flexion of the shoulders and right hip, and there was subtle swelling of the shoulders and right knee. Pitting edema (3+) and vitiligo were noted on the legs. No sclerodactyly, digital pitting, telangiectasias, appreciable calcinosis, nodules, nail changes (including pitting), or tophi were present. The remainder of the examination was normal.

The blood levels of glucose, alanine aminotransferase, aspartate aminotransferase, bilirubin, globulin, lactate, lipase, magnesium, and phosphorus were normal, as were the prothrombin time and international normalized ratio; other laboratory test results are shown in Table 1. Urinalysis showed 3+ protein and 3+ blood, and microscopic examination of the sediment revealed 5 to 10 red cells per high-power field and granular casts. Urine and blood were obtained for culture. An electrocardiogram met (at a borderline level) the voltage criteria for left ventricular hypertrophy.

Dr. Rene Balza Romero: Computed tomography (CT) of the chest, abdomen, and pelvis, performed after the intravenous administration of contrast material, revealed scattered subcentimeter pulmonary nodules (including clusters in the right middle lobe and patchy and ground-glass opacities in the left upper lobe), trace pleural effusion in the left lung, coronary and valvular calcifications, and trace pericardial effusion, ascites, and anasarca. The scans also showed slight enlargement of the axillary lymph nodes (up to 11 mm in the short axis) bilaterally and a chronic-appearing compression fracture involving the T12 vertebral body.
Dr. Parsons: Morphine and lactated Ringer’s solution were administered intravenously. On the second day in the emergency department (also referred to as hospital day 2), the blood levels of haptoglobin, folate, and vitamin B12 were normal; other laboratory test results are shown in Table 1. A rapid antigen test for malaria was positive. Wright–Giemsa staining of thick and thin peripheral-blood smears was negative for parasites; the smears also showed Döhle bodies and basophilic stippling. Antigliadin antibodies and anti–tissue transglutaminase antibodies were not detected. Tests for hepatitis A IgG and hepatitis C antibodies were positive. Tests for hepatitis B core and surface antibodies were negative. A test for human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) and type 2 (HIV-2) was negative.
Findings on abdominal ultrasound imaging performed on the second day (Fig. 2A and 2B) were notable for a small volume of ascites and kidneys with echogenic parenchyma. Ultrasonography of the legs showed no deep venous thrombosis. An echocardiogram showed normal ventricular size and function, aortic sclerosis with mild aortic insufficiency, moderate tricuspid regurgitation, a right ventricular systolic pressure of 39 mm Hg, and a small circumferential pericardial effusion. Intravenous hydromorphone was administered, and the patient was admitted to the hospital.

On the third day (also referred to as hospital day 3), nucleic acid testing for cytomegalovirus, Epstein–Barr virus, and hepatitis C virus was negative, and a stool antigen test for Helicobacter pylori was negative. An interferon-γ release assay for Mycobacterium tuberculosis was also negative. Oral acetaminophen and ivermectin and intravenous hydromorphone and furosemide were administered.
Dr. Balza Romero: Radiographs of the hands (Fig. 2C through 2F) showed joint-space narrowing of both radiocarpal joints and proximal interphalangeal erosions involving both hands. Radiographs of the shoulders showed arthritis of the glenohumeral joint and alignment suggestive of a tear of the right rotator cuff. A radiograph of the pelvis showed diffuse joint-space narrowing of the left hip, without osteophytosis, and an intact right hip prosthesis.
Dr. Parsons: Diagnostic tests were performed, and management decisions were made.

Final Diagnosis
Overlap syndrome of rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus complicated by proliferative lupus nephritis, superimposed on amyloid A amyloidosis.
 0
0

以下内容来源于PubMed。
Abstract
Sacituzumab govitecan (SG) significantly improved progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) versus chemotherapy in hormone receptor-positive human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-negative (HR+HER2-) metastatic breast cancer (mBC) in the global TROPiCS-02 study. TROPiCS-02 enrolled few Asian patients. Here we report results of SG in Asian patients with HR+HER2- mBC from the EVER-132-002 study. Patients were randomized to SG (n = 166) or chemotherapy (n = 165). The primary endpoint was met: PFS was improved with SG versus chemotherapy (hazard ratio of 0.67, 95% confidence interval 0.52-0.87; P = 0.0028; median 4.3 versus 4.2 months). OS also improved with SG versus chemotherapy (hazard ratio of 0.64, 95% confidence interval 0.47-0.88; P = 0.0061; median 21.0 versus 15.3 months). The most common grade ≥3 treatment-emergent adverse events were neutropenia, leukopenia and anemia. SG demonstrated significant and clinically meaningful improvement in PFS and OS versus chemotherapy, with a manageable safety profile consistent with prior studies. SG represents a promising treatment option for Asian patients with HR+HER2- mBC (ClinicalTrials.gov identifier no. NCT04639986 ).
 0
0

以下内容来源于PubMed。
Abstract
Irritable bowel syndrome with diarrhea (IBS-D) is a common and chronic gastrointestinal disorder that is characterized by abdominal discomfort and occasional diarrhea. The pathogenesis of IBS-D is thought to be related to a combination of factors, including psychological stress, abnormal muscle contractions, and inflammation and disorder of the gut microbiome. However, there is still a lack of comprehensive analysis of the logical regulatory correlation among these factors. In this study, we found that stress induced hyperproduction of xanthine and altered the abundance and metabolic characteristics of Lactobacillus murinus in the gut. Lactobacillus murinus-derived spermidine suppressed the basal expression of type I interferon (IFN)-α in plasmacytoid dendritic cells by inhibiting the K63-linked polyubiquitination of TRAF3. The reduction in IFN-α unrestricted the contractile function of colonic smooth muscle cells, resulting in an increase in bowel movement. Our findings provided a theoretical basis for the pathological mechanism of, and new drug targets for, stress-exposed IBS-D.
Keywords: AdorA2B; Lactobacillus murinus; irritable bowel syndrome with diarrhea; spermidine; stress; type I interferon; xanthine.
 0
0

Abstract
The severe bronchiolitis endotype characterized by a high abundance of H. influenzae, high proportion of RV-A and RV-C infections, and high asthma genetic risk had a significantly higher risk for developing asthma.
Background: Infants with bronchiolitis are at increased risk for developing asthma. Growing evidence suggests bronchiolitis is a heterogeneous condition. However, little is known about its biologically distinct subgroups based on the integrated metagenome and asthma genetic risk signature and their longitudinal relationships with asthma development.
Methods: In a multi-center prospective cohort study of infants with severe bronchiolitis (i.e., bronchiolitis requiring hospitalization), we profiled nasopharyngeal airway metagenome and virus at hospitalization, and calculated the polygenic risk score of asthma. Using similarity network fusion clustering approach, we identified integrated metagenome-asthma genetic risk endotypes. We also examined their longitudinal association with the risk of developing asthma by age six years.
Results: Of 450 infants with bronchiolitis (median age, 3 months), we identified five distinct endotypes-characterized by their nasopharyngeal metagenome, virus, and asthma genetic risk profiles. Compared with endotype A infants (who clinically resembled "classic" bronchiolitis), endotype E infants (characterized by a high abundance of H. influenzae, high proportion of RV-A and RV-C infections, and high asthma genetic risk) had a significantly higher risk for developing asthma (35.9% versus 16.7%; ORadj, 2.24; 95%CI, 1.02-4.97; p=0.046). The pathway analysis showed that endotype E had enriched microbial pathways (e.g., glycolysis, L-lysine, arginine metabolism) and host pathways (e.g., IFNs, IL-6/JAK/STAT3, fatty acids, MHC, and immunoglobin-related) (FDR<0.05). Additionally, endotype E had a significantly higher proportion of neutrophils (FDR<0.05).
Conclusion: In this multi-center prospective cohort study of infant bronchiolitis, the clustering analysis of integrated-omics data identified biologically distinct endotypes with differential risks for developing asthma.